How Many Hours Is 6am To 5pm
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
 | |
 Screenshot of Windows Server 2008 showing the Server Director application which is automatically opened when an administrator logs on. | |
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Microsoft Windows |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing | February 4, 2008 (2008-02-04) [i] |
| Full general availability | February 27, 2008 (2008-02-27) [1] |
| Latest release | Service Pack 2 with March 19, 2019 or later update rollup (half-dozen.0.6003)[2] / March xix, 2019 (2019-03-19) |
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium |
| Kernel blazon | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface | Windows shell (Graphical) |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2003 (2003) |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Server 2008 |
| Back up status | |
| Mainstream back up concluded on January xiii, 2015[3] [4] Extended back up ended on January 14, 2020[iii] [4] Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid ESU (Extended Security Updates) plan (free for Azure Virtual Desktop users).[v] This program allows volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system through at virtually January 10, 2023 (January 9, 2024 for Azure customers),[3] but for Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter volume licensed editions.[half-dozen] [5] [7] Installing Service Pack 2 is required for users to receive updates and support afterward July 12, 2011[3] [4] | |
Windows Server 2008 is the quaternary release of the Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft as office of the Windows NT family unit of the operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and generally to retail on February 27, 2008. Derived from Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 is the successor of Windows Server 2003 and the predecessor to Windows Server 2008 R2.
On January 12, 2016, Microsoft ended back up for all Net Explorer versions older than Internet Explorer 11 released in 2013 for Windows 7. Extended support for Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020.[iii] [4]
Extended Security Updates (ESU) updates last until January 10, 2023 (January 9, 2024 for Azure customers).[8]
Windows Server 2008 is the final version which supports IA-32-based processors (also known as 32-bit processors). Its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2, requires a 64-bit processor in any supported architecture (x86-64 for x86 and Itanium).
History [edit]
Microsoft had released Windows Vista to mixed reception, and their terminal Windows Server release| was based on Windows XP. The operating organisation's working title was Windows Server Codename "Longhorn", but was later inverse to Windows Server 2008 when Microsoft chairman Neb Gates announced it during his keynote address at WinHEC 16 May 2007.[9]
Beta one was released on July 27, 2005; Beta 2 was announced and released on May 23, 2006, at WinHEC 2006 and Beta 3 was released publicly on Apr 25, 2007.[10] Release Candidate 0 was released to the general public on September 24, 2007[11] and Release Candidate ane was released to the general public on December 5, 2007. Windows Server 2008 was released to manufacturing on February iv, 2008, and officially launched on 27th of that month.[12]
Features [edit]
Windows Server 2008 is congenital from the same codebase equally Windows Vista and thus it shares much of the same architecture and functionality. Since the codebase is common, Windows Server 2008 inherits almost of the technical, security, direction and authoritative features new to Windows Vista such every bit the rewritten networking stack (native IPv6, native wireless, speed and security improvements); improved image-based installation, deployment and recovery; improved diagnostics, monitoring, outcome logging and reporting tools; new security features such as BitLocker and address infinite layout randomization (ASLR); the improved Windows Firewall with secure default configuration; .Net Framework 3.0 technologies, specifically Windows Communication Foundation, Microsoft Message Queuing and Windows Workflow Foundation; and the cadre kernel, retentiveness and file system improvements. Processors and retention devices are modeled every bit Plug and Play devices to allow hot-plugging of these devices. This allows the arrangement resource to be partitioned dynamically using dynamic hardware partitioning - each partition has its own memory, processor and I/O host bridge devices independent of other partitions.[13]
Server Core [edit]
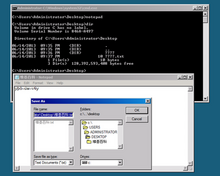
Windows Server 2008 includes a variation of installation called Server Cadre. Server Core is a significantly scaled-dorsum installation where no Windows Explorer shell is installed. It also lacks Internet Explorer, and many other non-essential features. All configuration and maintenance is done entirely through control-line interface windows, or by connecting to the machine remotely using Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Notepad and some Control Panel applets, such equally Regional Settings, are available.
A Server Core installation can be configured for several basic roles, including the domain controller (Agile Directory Domain Services), Agile Directory Lightweight Directory Services (formerly known as Active Directory Application Mode[14]), DNS Server, DHCP server, file server, print server, Windows Media Server, Cyberspace Information Services 7 web server and Hyper-V virtual server roles. Server Cadre can also be used to create a cluster with loftier availability using failover clustering or network load balancing.
Andrew Bricklayer, a plan manager on the Windows Server team, noted that a main motivation for producing a Server Cadre variant of Windows Server 2008 was to reduce the assail surface of the operating system, and that about 70% of the security vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows from the prior five years would not have affected Server Core.[15]
Active Directory [edit]
The Active Directory domain functionality that was retained from Windows Server 2003 was renamed to Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS).[16]
- Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) enables enterprises to share credentials with trusted partners and customers, assuasive a consultant to use their company user name and password to log in on a client'due south network.
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), (formerly Active Directory Application Mode, or ADAM)
- Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) allow administrators to manage user accounts and the digital certificates that let them to admission sure services and systems. Identity Integration Characteristic Pack is included equally Active Directory Metadirectory Services.
- Agile Directory Rights Management Services (ADRMS)
- Read-merely domain controllers (RODCs), intended for use in branch office or other scenarios where a domain controller may reside in a low physical security surround. The RODC holds a not-writeable copy of Active Directory, and redirects all write attempts to a total domain controller. It replicates all accounts except sensitive ones.[17] In RODC style, credentials are non cached by default. Likewise, local administrators tin can be designated to log on to the car to perform maintenance tasks without requiring administrative rights on the entire domain.[18]
- Restartable Active Directory allows ADDS to be stopped and restarted from the Direction Panel or the command-line without rebooting the domain controller. This reduces downtime for offline operations and reduces overall DC servicing requirements with Server Core. ADDS is implemented as a Domain Controller Service in Windows Server 2008.
- All of the Grouping Policy improvements from Windows Vista are included. Group Policy Direction Console (GPMC) is built-in. The Group Policy objects are indexed for search and can be commented on.[19]
- Policy-based networking with Network Access Protection, improved branch management and enhanced terminate user collaboration. Policies can be created to ensure greater quality of service for sure applications or services that require prioritization of network bandwidth betwixt client and server.
- Granular password settings within a unmarried domain - ability to implement unlike password policies for administrative accounts on a "group" and "user" basis, instead of a single set of password settings to the whole domain.
Failover Clustering [edit]
Windows Server 2008 offers high availability to services and applications through Failover Clustering. Most server features and roles tin can exist kept running with little to no downtime.
In Windows Server 2008, the way clusters are qualified changed significantly with the introduction of the cluster validation wizard.[20] The cluster validation wizard is a feature that is integrated into failover clustering in Windows Server 2008. With the cluster validation wizard, an administrator tin run a set of focused tests on a collection of servers that are intended to use equally nodes in a cluster. This cluster validation process tests the underlying hardware and software directly, and individually, to obtain an accurate cess of how well failover clustering can be supported on a given configuration.
This feature is only available in Enterprise and Datacenter editions of Windows Server.
Deejay management and file storage [edit]
- The ability to resize hd partitions without stopping the server, even the system sectionalisation. This applies only to simple and spanned volumes, not to striped volumes.
- Shadow Copy based cake-level backup which supports optical media, network shares and Windows Recovery Environment.
- DFS enhancements - SYSVOL on DFS-R, Read-only Folder Replication Fellow member. At that place is as well support for domain-based DFS namespaces that exceed the previous size recommendation of 5,000 folders with targets in a namespace.[21]
- Several improvements to Failover Clustering (loftier-availability clusters).[22]
- Internet Storage Naming Server (iSNS) enables key registration, deregistration and queries for iSCSI difficult drives.
- Self-healing NTFS: In Windows versions prior to Windows Vista, if the operating organisation detected corruption in the file system of an NTFS book, it marked the volume "dirty"; to correct errors on the book, information technology had to be taken offline. With self-healing NTFS, an NTFS worker thread is spawned in the groundwork which performs a localized set-upwards of damaged data structures, with just the corrupted files/folders remaining unavailable without locking out the entire book and needing the server to be taken downward. South.M.A.R.T. detection techniques were added to assist decide when a hard disk may neglect.[23]
Hyper-V [edit]
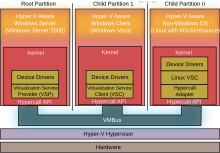
Hyper-5 is hypervisor-based virtualization software, forming a core part of Microsoft'southward virtualization strategy. It virtualizes servers on an operating system's kernel layer. It can exist thought of equally partitioning a single physical server into multiple small computational partitions. Hyper-5 includes the power to act as a Xen virtualization hypervisor host allowing Xen-enabled invitee operating systems to run virtualized.[24] A beta version of Hyper-V shipped with sure x86-64 editions of Windows Server 2008, prior to Microsoft's release of the final version of Hyper-V on 26 June 2008 every bit a complimentary download. Also, a standalone variant of Hyper-Five exists; this variant supports only x86-64 architecture.[25] While the IA-32 editions of Windows Server 2008 cannot run or install Hyper-V, they can run the MMC snap-in for managing Hyper-V.
Windows System Resource Managing director [edit]
Windows Arrangement Resource Manager (WSRM) is integrated into Windows Server 2008. It provides resources management and tin be used to control the corporeality of resources a process or a user tin employ based on business priorities. Process Matching Criteria, which is defined past the name, type or owner of the procedure, enforces restrictions on the resources usage past a process that matches the criteria. CPU time, bandwidth that information technology tin utilize, number of processors information technology tin exist run on, and allocated to a procedure tin exist restricted. Restrictions can be fix to be imposed simply on certain dates as well.
Server Director [edit]
Server Manager is a new roles-based management tool for Windows Server 2008.[26] It is a combination of Manage Your Server and Security Configuration Wizard from Windows Server 2003. Server Managing director is an improvement of the Configure my server dialog that launches by default on Windows Server 2003 machines. However, rather than serve only as a starting point to configuring new roles, Server Manager gathers together all of the operations users would want to conduct on the server, such as, getting a remote deployment method ready, calculation more server roles etc., and provides a consolidated, portal-similar view about the status of each role.[27]
Protocol and cryptography [edit]
- Support for 128- and 256-bit AES encryption for the Kerberos authentication protocol.
- New cryptography (CNG) API which supports elliptic curve cryptography and improved certificate direction.
- Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol, a new Microsoft proprietary VPN protocol.
- AuthIP, a Microsoft proprietary extension of the IKE cryptographic protocol used in IPsec VPN networks.
- Server Bulletin Cake 2.0 protocol in the new TCP/IP stack provides a number of communication enhancements, including greater performance when connecting to file shares over loftier-latency links and better security through the apply of common authentication and bulletin signing.
Miscellaneous [edit]
- Fully componentized operating system.
- Improved hot patching, a feature that allows non-kernel patches to occur without the need for a reboot.
- Back up for being booted from Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI)-compliant firmware on x86-64 systems.
- Dynamic Hardware Partitioning supports hot-improver or replacement of processors and retentivity, on capable hardware.
- Windows Deployment Services (WDS) replacing Automated Deployment Services Windows Server 2008 dwelling amusement and Remote Installation Services. Windows Deployment Services supports an enhanced multicast feature when deploying operating organisation images.[28]
- Internet Information Services seven - Increased security, Robocopy deployment, improved diagnostic tools, delegated assistants.
- Windows Internal Database, a variant of SQL Server Express 2005, which serves every bit a mutual storage back-end for several other components such as Windows System Resource Director, Windows SharePoint Services and Windows Server Update Services. It is not intended to be used by third-party applications.
- An optional "desktop experience" component provides the same Windows Aero user interface equally Windows Vista, both for local users, as well as remote users connecting through Remote Desktop.
Removed features [edit]
- The Open Shortest Path Commencement (OSPF) routing protocol component in Routing and Remote Access Service was removed.[29]
- Services for Macintosh, which provided file and print sharing via the now deprecated AppleTalk protocol, has been removed. Services for Macintosh were initially removed in Windows XP only were available in Windows Server 2003.[29]
- NTBackup is replaced by Windows Server Fill-in, and no longer supports bankroll up to tape drives.[xxx] As a effect of NTBackup removal, Exchange Server 2007 does not have volume snapshot backup functionality; however Exchange Server 2007 SP2 adds back an Commutation fill-in plug-in for Windows Server Fill-in which restores partial functionality.[31] Windows Small Business Server and Windows Essential Business Server both include this Commutation backup component.[32]
- The POP3 service has been removed from Net Information Services 7.0.[33] The SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) service is not available every bit a server office in IIS 7.0, it is a server characteristic managed through IIS half dozen.0.
- NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) is no longer part of Internet Data Services seven.0.
- ReadyBoost, which is available in Windows Vista, is non supported in Windows Server 2008.
Support lifecycle [edit]
Support for the RTM version of Windows Server 2008 ended on July 12, 2011,[3] [iv] and users can no longer receive farther security updates for the operating arrangement. As a component of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 with Service Pack 2 continued to be supported with security updates, lasting until January 14, 2020, the same respective end-of-life dates of its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows vii.
Microsoft planned to end support for Windows Server 2008 on Jan 12, 2016. Still, in society to give customers more time to migrate to newer Windows versions, specially in developing or emerging markets, Microsoft decided to extend support until January 14, 2020.[6] [5] [7] That date marked the final end of the Windows Vista codebase afterward xiii years, 2 month and 6 days. In 2018, Microsoft appear the Extended Security Updates (ESU) service for Windows Server 2008/R2 to requite users iii additional years of security patches. Security updates are available for the operating system until January ten, 2023. In November 2021 Microsoft reported if ESU service is installed on Microsoft Azure, it'll accept additional year of back up, beginning on January xi, 2023 and ending on January ix, 2024.[8] In the case of Azure, this will mark the last end of the Extended Security Updates support for Windows Vista codebase after 17 years, 2 months, and ane day.
Windows Server 2008 can be upgraded to Windows Server 2008 R2 on 64-bit systems only.
Editions [edit]

Installation disc of Enterprise edition (beta 3)
Most editions of Windows Server 2008 are available in x86-64 and IA-32 variants. These editions come in 2 DVDs: 1 for installing the IA-32 variant and the other for x64. Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems supports IA-64 processors. The IA-64 variant is optimized for high-workload scenarios like database servers and Line of Business organisation (LOB) applications. Equally such, it is not optimized for use as a file server or media server. Windows Server 2008 is the concluding 32-bit Windows server operating organisation.[34] Editions of Windows Server 2008 include:[35]
- Windows Server 2008 Foundation (codenamed "Lima"; x86-64) for OEMs merely[36]
- Windows Server 2008 Standard (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Enterprise (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Datacenter (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems (IA-64)
- Windows Web Server 2008 (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows HPC Server 2008 (codenamed "Socrates"; replacing Windows Compute Cluster Server)
- Windows Storage Server 2008 (codenamed "Magni"; IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Small Business Server 2008 (codenamed "Cougar"; x86-64) for minor businesses
- Windows Essential Business Server 2008 (codenamed "Centro"; x86-64) for medium-sized businesses[37] - this edition was discontinued in 2010.[38]
The Microsoft Imagine plan, known as DreamSpark at the fourth dimension, used to provide verified students with the 32-scrap variant of Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition, but the version has since so been removed. Still, they still provide the R2 release.
The Server Core feature is available in the Web, Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter editions.
Windows Server 2008 Foundation Released on May 21, 2009.[39]
Updates [edit]
Windows Server 2008 shares most of its updates with Windows Vista due to being based on that operating system'due south codebase. A workaround was found that allowed the installation of updates for Windows Server 2008 on Windows Vista,[40] adding three years of security updates to that operating system (Back up for Windows Vista ended on April 11, 2017,[41] while support for Windows Server 2008 concluded on Jan 14, 2020).
Service Pack ii [edit]
Due to the operating system beingness based on the same codebase equally Windows Vista and being released on the same day as the initial release of Windows Vista Service Pack 1, the RTM release of Windows Server 2008 already includes the updates and fixes of Service Pack 1.
Service Pack 2 was initially announced on October 24, 2008[42] and released on May 26, 2009. Service Pack 2 added new features, such as Windows Search 4.0, support for Bluetooth 2.1, the ability to write to Blu-ray discs, and simpler Wi-Fi configuration. Windows Server 2008 specifically received the concluding release of Hyper-V 1.0, improved backwards compatibility with Final Server license keys and an approximate x% reduction in power usage with this service pack.[43]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 share the same service pack update binary considering the codebases of the ii operating systems are unified - Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 are the outset Microsoft client and server operating systems to share the aforementioned codebase since the release of Windows 2000.[44] The predecessors to Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, had unique codebases that used their own updates and service packs.
Platform Update [edit]
On October 27, 2009, Microsoft released the Platform Update for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista. It backports several APIs and libraries introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 to Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista, including the Ribbon API, DirectX 11, the XPS library, the Windows Automation API and the Portable Device Platform.[45] A supplemental update was released in 2011 to provide improvements and bug fixes.[46]
Net Explorer 9 [edit]
Windows Server 2008 shipped with Internet Explorer 7, the aforementioned version that shipped with Windows Vista. The concluding supported version of Internet Explorer for Windows Server 2008 is Internet Explorer 9, released in 2011. Internet Explorer 9 was continually updated with cumulative monthly update rollups until support for Cyberspace Explorer nine on Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020.[47] Extended Security Updates (ESU) last for the operating organisation and IE9 until January 10, 2023 (Jan nine, 2024 for Azure customers), marking the end of an era of older versions of Cyberspace Explorer than IE11.
.Net Framework [edit]
The latest supported version of the .NET Framework officially is version 4.6, released on Oct xv, 2015.[48]
TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support [edit]
In July 2017, Microsoft released an update to add TLS 1.1 and 1.2 back up to Windows Server 2008, however it is disabled by default subsequently installing the update.[49]
SHA-2 signing back up [edit]
Starting in March 2019, Microsoft began transitioning to exclusively signing Windows updates with the SHA-2 algorithm. Every bit a effect of this Microsoft released several updates throughout 2019 to add SHA-ii signing support to Windows Server 2008.[fifty]
Monthly update rollups [edit]
In June 2018, Microsoft announced that they would be moving Windows Server 2008 to a monthly update model start with updates released in September 2018[51] - two years later Microsoft switched the rest of their supported operating systems to that model.[52]
With the new update model, instead of updates being released every bit they became bachelor, only ii update packages were released on the second Tuesday of every month until Windows Server 2008 reached its end of life - one package containing security and quality updates, and a smaller package that independent only the security updates. Users could choose which package they wanted to install each month. Later in the month, another package would be released which was a preview of the next calendar month's security and quality update rollup.
Installing the preview rollup package released for Windows Server 2008 on March xix, 2019, or any later released rollup package, will update the operating organisation kernel'southward build number from version six.0.6002 to 6.0.6003. This modify was made so Microsoft could proceed to service the operating arrangement while fugitive "version-related issues".[53]
The last complimentary security update rollup packages were released on Jan 14, 2020.[54]
Extended Security Updates [edit]
Windows Server 2008/R2 are eligible for the paid Extended Security Updates (ESU) program (gratis for Azure Virtual Desktop users). This plan allows volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating organization until at most iii years after end of extended support, for 4 years for Azure customers, lasting until Jan 10, 2023 (January ix, 2024 for Azure customers). The licenses are paid for on a per-machine basis. If a user purchases an Extended Security Updates license in a after year of the program, they must pay for any previous years of Extended Security Updates as well. Extended Security Updates are released just as they become available.[6]
Windows Server 2008 R2 [edit]
A 2nd release of Windows Server 2008 based on Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009[55] and became more often than not bachelor on October 22, 2009.[56] New features added in Windows Server 2008 R2 include new virtualization features, new Active Directory features, Internet Data Services 7.five and support for upwards to 256 logical processors. It is the first server operating system by Microsoft to exclusively back up 64-bit processors, a move which would exist followed by the consumer-oriented Windows 11 in 2021.
A service pack for Windows vii and Windows Server 2008 R2, formally designed Service Pack 1, was released in February 2011.[57]
System requirements [edit]
Arrangement requirements for Windows Server 2008 are every bit follows:
| Criteria | 2008 | 2008 R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum[58] | Recommended[58] | Minimum[59] | Recommended[59] | |
| CPU |
| two GHz or faster | 1.4 GHz (x86-64 or Itanium) | 2 GHz or faster |
| RAM | 512 MB | ii GB or greater | 512 MB | GB]] or greater |
| HDD[a] |
| forty GB or greater |
|
|
| Devices | DVD bulldoze, 800 × 600 or higher display, keyboard and mouse | |||
Scalability [edit]
Windows Server 2008 supports the following maximum hardware specifications:[61] [62] [63]
| Specification | Windows Server 2008 SP2 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Physical processors ("sockets")[62] |
|
|
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is disabled[62] |
| 256 |
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is enabled[62] |
| 64 |
| Memory on IA-32[63] |
| — |
| Memory on x64[63] |
|
|
| Retention on Itanium[63] | two TB | |
Meet besides [edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of Microsoft Windows
- List of operating systems
- Microsoft Servers
Notes [edit]
- ^ Computers with more 16 GB of RAM require more disk infinite for paging, hibernation, and dump files[59]
References [edit]
- ^ a b "As Windows Server 2008 RTMs, Customers and Partners Adopting with Help of New Tools, Training". News Center. Redmond, WA: Microsoft. 4 February 2008.
- ^ "Build number irresolute to 6003 in Windows Server 2008". support.microsoft.com . Retrieved 2021-03-26 .
- ^ a b c d east f "Microsoft Product Lifecycle". Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e "Install Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2)". Back up. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2010.
- ^ a b c "Extended Security Updates for SQL Server and Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 | Microsoft". world wide web.microsoft.com . Retrieved 2021-03-26 .
- ^ a b c tfosmark. "Production Lifecycle FAQ - Extended Security Updates - Microsoft Lifecycle". docs.microsoft.com . Retrieved 2021-03-26 .
- ^ a b "Announcing new options for SQL Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 End of Support". azure.microsoft.com . Retrieved 2021-03-26 .
- ^ a b "Windows Server 2008 Product Lifecycle". Microsoft. January fourteen, 2020. Retrieved January 9, 2022.
18:55
- ^ Miller, Michael J. (2007-05-15). "Gates at WinHec 2007: Windows Server 2008, Rally, Home Server and More". Forward Thinking . Retrieved 2007-07-09 .
- ^ Lowe, David (2007-04-25). "Beta 3 is Become!". Windows Server Partition WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-04-25 .
- ^ Ralston, Ward (2007-09-24). "Windows Server 2008 Rc0 Released!". Windows Server Partition Web log. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-09-24 .
- ^ Nate Mook (10 July 2007). "New Windows Server, Visual Studio, SQL Server to Launch in Feb". BetaNews. Retrieved 2007-07-11 . It is besides ordinarily referred to as Vista Server.
- ^ "Dynamic Hardware Partitioning Architecture". MSDN. Retrieved 2007-07-23 .
- ^ Archiveddocs. "Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services Overview". docs.microsoft.com . Retrieved 2020-01-15 .
- ^ "Iain McDonald and Andrew Mason show off the new Windows Server OS". Channel nine. Microsoft. May 24, 2006. Retrieved 2008-11-01 .
18:55
- ^ Hynes, Byron (Nov 2006). "The Future of Windows: Directory Services in Windows Server 2008". TechNet Mag . Retrieved 2007-05-02 .
- ^ "Deploying Windows Server 2008 Read Only Domain Controllers". docs.microsoft.com . Retrieved 2020-01-xv .
- ^ "Q. What is a read-but domain controller (RODC)?". IT Pro. 2008-03-24. Retrieved 2020-01-15 .
- ^ Ward, Keith (2007-x-08). "Pinnacle ten Overlooked Windows Server 2008 Features, Part 2". Redmond Developer News. Archived from the original on 2009-08-04. Retrieved 2014-10-ten .
- ^ "Failover Cluster Validation Error 80070005 on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64". Capitalhead. 2009-11-04. Retrieved 2013-x-28 .
- ^ Zoeller, Jill (26 July 2007). "New in Windows Server 2008: Breaking the 5K Folder "Barrier" in Domain-Based Namespaces". The Storage Team at Microsoft - File Cabinet Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved xvi August 2013.
- ^ "Failover Clustering with Windows Server 2008 including Cluster shared volumes". Microsoft. 2007-01-17. Retrieved 2007-07-09 .
- ^ Loveall, John (2006). "Storage improvements in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008" (PowerPoint). Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved 2007-07-09 .
- ^ "Benchmarking Hyper-V on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64". 2010-01-20. Retrieved 2010-01-28 .
- ^ "Microsoft Extends Virtualization Strategy, Outlines Product Road Map". Microsoft. 2006-05-22. Retrieved 2007-07-09 .
- ^ "Server Managing director". Windows Server 2008 Technical Library. Microsoft TechNet. 2007-06-25. Retrieved 2007-05-02 .
- ^ "Unexpected error refreshing Server Manager-0x800706BE and 1601 on Window Server 2008 R2". Retrieved 2010-11-05 .
- ^ "Multicasting Os deployments with Windows Server 2008". Kevinsul's Management Blog. Microsoft. 29 Baronial 2007. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ a b "Removed technologies in Routing and Remote Access in Windows Server 2008". TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 Baronial 2013.
- ^ "Windows Server Fill-in Step-by-Step Guide for Windows Server 2008". TechNet. Microsoft. 17 January 2013. Retrieved 16 Baronial 2013.
- ^ "Exchange Server 2007 Service Pack 2 available in Q3 2009". The Commutation Team Blog. 11 May 2009. Retrieved sixteen August 2013.
- ^ Bilic, Nino (eighteen June 2008). "To Backup or Not to Backup? Yes! To backup!!". The Commutation Team Blog . Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ "IIS vii.0 Protocols". TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Heaton, Alex (2007-05-18). "On 64-bit and Windows Customer". Windows Vista Team Weblog . Retrieved 2007-07-09 .
- ^ "Windows Server 2008 Product Editions". Microsoft. 2007-04-25. Retrieved 2007-07-09 .
- ^ "Windows Server 2008 Foundation: An Entry-Level Server Platform". Petri IT Knowledgebase. 2009-04-17. Retrieved 2014-01-08 .
- ^ Ligman, Eric (vii November 2007). "Announcing Windows Essential Business organisation Server". Microsoft Modest Business Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-08-16 .
- ^ "Windows Essential Business Server 2008". Technet.microsoft.com. 2010-12-31. Retrieved 2013-01-09 .
- ^ "Windows Server 2008, Microsoft Lifecycle (Await at the Notation below links)". docs.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/products/.
- ^ "Extend Windows Vista support by installing Windows Server 2008 updates - gHacks Tech News". gHacks Technology News. 2017-06-24. Retrieved 2021-06-thirty .
- ^ "Windows Vista Lifecycle Policy". Microsoft. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Justin Graham (October 24, 2008). "Windows Server 2008 Service Pack ii beta". Microsoft. Retrieved 2008-10-29 .
- ^ "Tech ARP - ED#107 : Latest Details on Windows Vista Service Pack ii Rev. ii.2". Archived from the original on 2009-02-12.
- ^ "Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta". blogs.windows.com. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 12 Jan 2022.
- ^ "Announcing Last Releases of Platform Update for Windows Vista Technologies". 27 October 2009.
- ^ "Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and for Windows Server 2008".
- ^ "Cumulative security update for Internet Explorer: January 14, 2020". support.microsoft.com . Retrieved 2021-03-26 .
- ^ "Microsoft .NET Framework 4.6 (Web Installer)". Microsoft.
- ^ "TLS 1.2 Support added to Windows Server 2008". Microsoft Security. 2017-07-20. Retrieved 2021-03-26 .
- ^ "2019 SHA-2 Lawmaking Signing Support requirement for Windows and WSUS".
- ^ Mackie, Kurt; 06/thirteen/2018. "Microsoft Switching Windows Server 2008 SP2 to Monthly Update Rollup Model -- Redmondmag.com". Redmondmag . Retrieved 2021-03-26 .
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors listing (link) - ^ "Community". forums.ivanti.com . Retrieved 2021-03-26 .
- ^ "Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008".
- ^ "January fourteen, 2020—KB4534303 (Monthly Rollup)". support.microsoft.com . Retrieved 2021-03-26 .
- ^ "Windows Server 2008 R2 Reaches the RTM Milestone! - Windows Server Blog - Site Home - TechNet Blogs". Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09 .
- ^ "When to expect Windows Server 2008 R2 RTM - Windows Server Blog - Site Home - TechNet Blogs". Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09 .
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (February 9, 2011). "Announcing Availability of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1". Windows Feel Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ a b "Windows Server 2008 System Requirements". 31 March 2008. Retrieved 2008-03-31 .
- ^ a b c "Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements". Microsoft.com. Retrieved 2013-01-09 .
- ^ "Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Arrangement Requirements". Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-01-09 .
- ^ Savill, John (October 28, 2011). "Q: What are Windows Server 8's Scalability Numbers?". Windows It Pro. Penton Media. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ a b c d Seldam, Matthijs ten (Oct xiii, 2012). "Windows Server - Sockets, Logical Processors, Symmetric Multi Threading". Matthijs's blog. Microsoft. Retrieved October 14, 2012.
- ^ a b c d "Retention Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases". MSDN. Microsoft. Retrieved 13 Apr 2014.
Further reading [edit]
- "What's New in Networking". TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 Baronial 2013.
- "Changes in Functionality from Windows Server 2003 with SP1 to Windows Server 2008". TechNet. Microsoft. 21 January 2008. Retrieved xvi August 2013.
- "Description of the Microsoft server applications that are supported on Windows Server 2008". Support. Microsoft. 23 April 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- "Windows Server 2008 System Requirements". TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved xvi August 2013.
- Henderson, Tom; Dvorak, Rand (21 February 2008). "Windows Server 2008: Faster, more than manageable and secure, just still missing the virtual link". Network World. IDG. Retrieved xvi Baronial 2013.
- Radzikowski, Przemek (21 Feb 2010). "How to Find Build and Revision Number of Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 Installed". Capitalhead. Capitalhead Pty. Ltd. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Stanek, William (2008). Windows Server 2008 Inside Out. Microsoft Press. ISBN978-0-7356-2438-two.
External links [edit]
- Windows Server Performance Squad Blog
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Windows_Server_2008

0 Response to "How Many Hours Is 6am To 5pm"
Post a Comment